Hi guys welcome to basics part 2 today we are going to see about MOSFET. Before going to know about MOSFET you must know about transistor.
What is a Transistor?
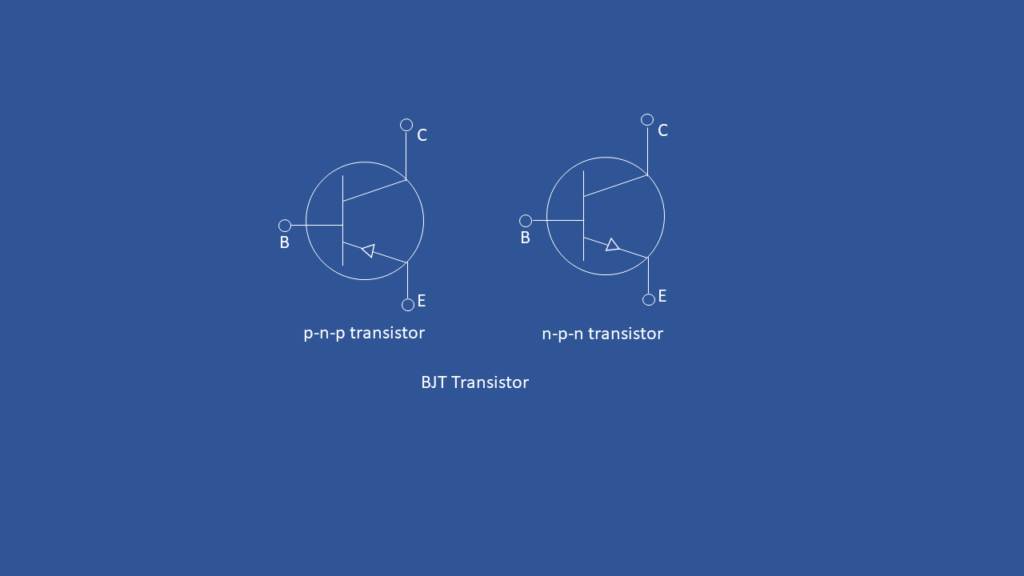
A transistor is a semiconductor device which has 3 terminals. It is used for switching as well as amplification.It is a current controlled device
The three terminals of the transistor are:
- Base
- Emitter
- Collector
Symbol of a Transistor
What is MOSFET?
MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor. It is also a semiconductor device consists of 4terminals.It is also used for switching as well as amplification purposes. It is a voltage controlled device.
The four terminals of the MOSFET are
- Gate
- Source
- Drain
- Body
In General the fourth terminal substarte or body is shorted to source so we consider only three terminals Base,Source,Drain.
Here you might get one doubt why we go for MOSFET even the Transistor also doing the same work the answer is there are numerous reasons are there some of them are less size, less power,high input impedence,less noise etc.
MOSFET’S are classified into two types
- Depletion Mode
- Enhancement Mode
Again each mode consists of two types of MOSFET’s
- PMOS
- NMOS
Depletion Mode MOSFET
The Depletion Mode MOSFET has channel was constructed during manufacturing process. Beacuse of this channel it conduct between its drain to source when the gate voltage Vgs is 0 volts. Hence its called as normally ON Transistor
Enhancement Mode MOSFET
The Enhancement Mode MOSFET works as quite opposite to Depletion Mode when there is no voltage across the gate terminal then it doesn’t conduct. It conducts only when the gate terminal has maximum voltage applied
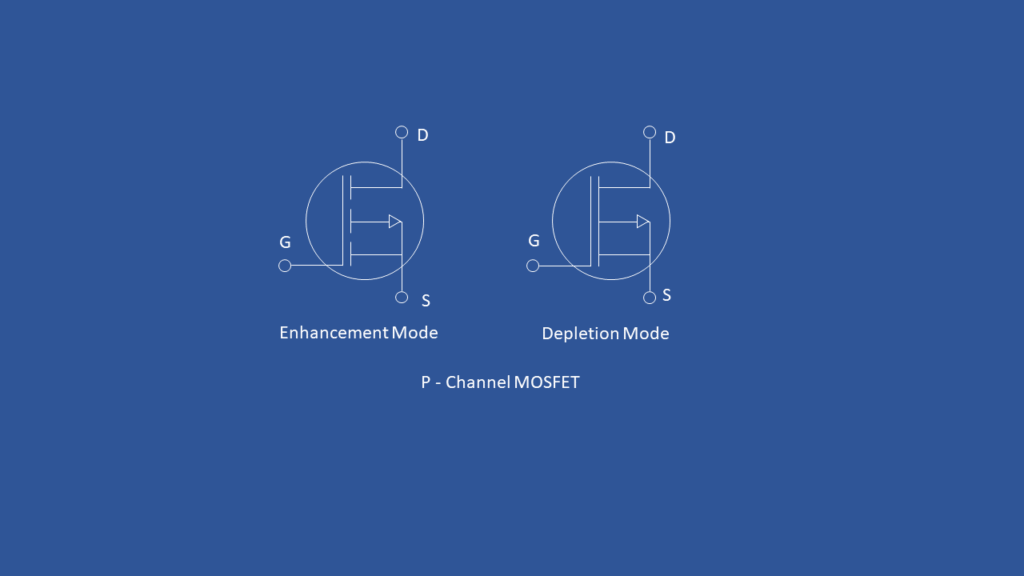
PMOS (Enhancement Mode)
In PMOS the source and drain terminals are P -type and substrate is N -type. PMOS will turned ON when the input is 0. Symbol of PMOS is shown below
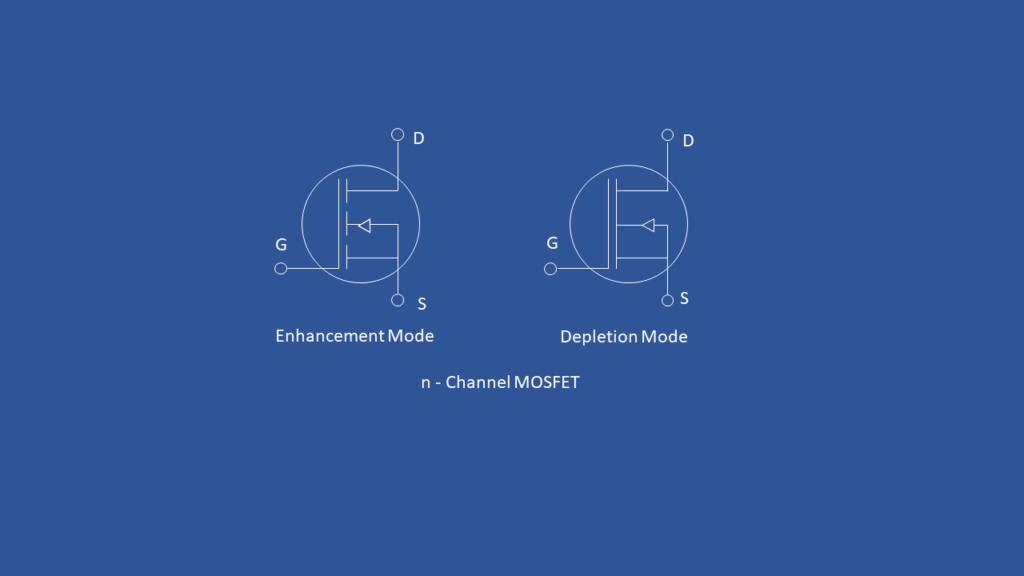
NMOS (Enhancement Mode)
In NMOS the source and drain terminals are N -type and substrate is P -type. NMOS will turned ON when the input is 1. Symbol of NMOS is shown below
Both PMOS and NMOS works as opposite to each other.
NOTE: The terminals of MOSFET are interchangeable there is no fixed terminal for Source and Drain. The terminal which has higher potential acts as source & which has low potential acts as drain
Operating Regions of MOSFET
The MOSFETS has three operating regions.They are
- Cut-off Region
- Ohmic or Triode Region
- Saturation Region
Let us discuss about each region in detail taking NMOS as example
Cut-off Region
As it name suggests that Cut-off it means it wont turned ON. Consider a NMOS which has gate voltage of 0 volts. In this condition it wont turned ON because Vgs ≥ Vth.
Don’t get scared while seeing those Vgs& Vth names I will don’t take you into derivations. Honestly speaking I’m also not like those derivation parts. Coming to topic
Vgs – Gate to Source Voltage
Vth – Threshold voltage
Threshold Voltage (Vth) is nothing but a minimum voltage required to turn ON the MOSFET. Every MOSFET has Threshold voltage if the Gate to Source Voltage (Vgs) is greater than or equal to threshold voltage then only the device will turned ON otherwise its in OFF state
Let us take one example
Consider the NMOS has Vthof 1v VDD 5V Now apply (0V& 5V) to gate and see when NMOS is turned ON
Case I :
Vg =0V
Vgs = Vg -Vs => 0 – 0 = 0V
Here, Vs is nothing but Voltage across at Source terminal i.e VSS = 0v
Vg is nothing but voltage across Gate terminal
Now check the condition
Vgs> Vth => 0V ≥1V (Condition fail )
Hence it is in Cut-off region
Case II:
Vg = 5V
Vgs = Vg -Vs => 5 – 0 = 5V
Now check the condition
Vgs> Vth => 5V ≥ 1V ( Condition true )
Hence its not in Cut-off region
Ohmic or Triode region
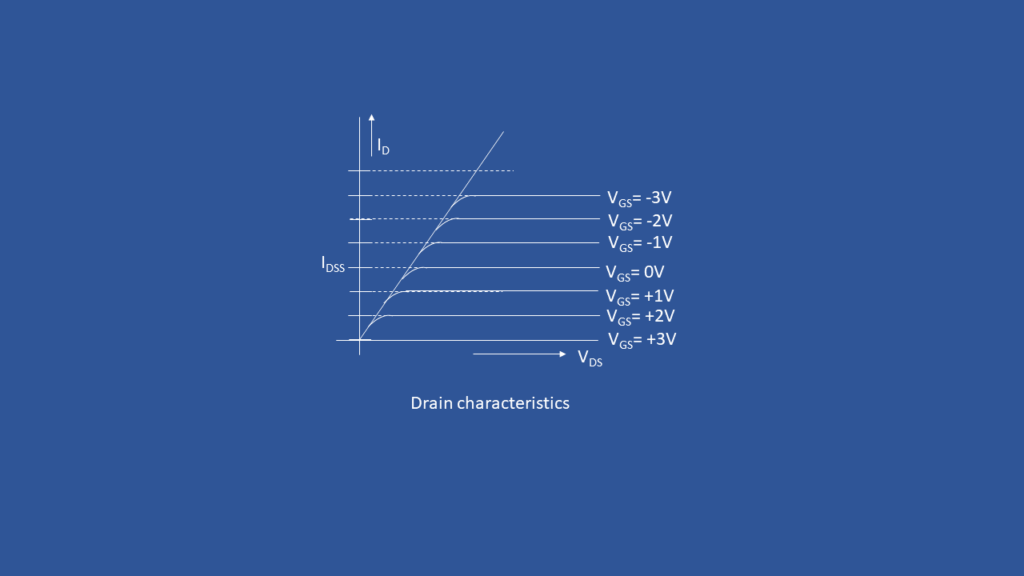
The ohmic region is a region where the current (IDS)increases with an increase in the value of Vds. In this region the channel was created due tothe voltage between gate & source(Vgs) is greater than the threshold voltage( Vth)
When the Vgs> Vth the device is in triode region or saturation depending upon the Vdsvalue
Vds < Vgs– Vth
Then the device is in Triode region
Saturation region
When Vgs > Vth
Vds > Vgs– Vth
Then the MOSFET is in saturation region.In this region the current no more depends on Vds. In saturation region the current Id doesn’t increase with increase in Vds. But current can increase if you increase the gate to source voltage Vgs. We use this region for amplifiers.
Equations
| PMOS | NMOS |
| Vsg < |Vt| | OFF | Vgs < Vt | OFF |
| Vsd < Vsg – |Vt| | LINEAR | Vds < Vgs -Vt | LINEAR |
| Vsd > Vsg – |Vt| | SATURATION | Vds > Vgs – Vt | SATURATION |
Transfer Characteristics of MOSFET
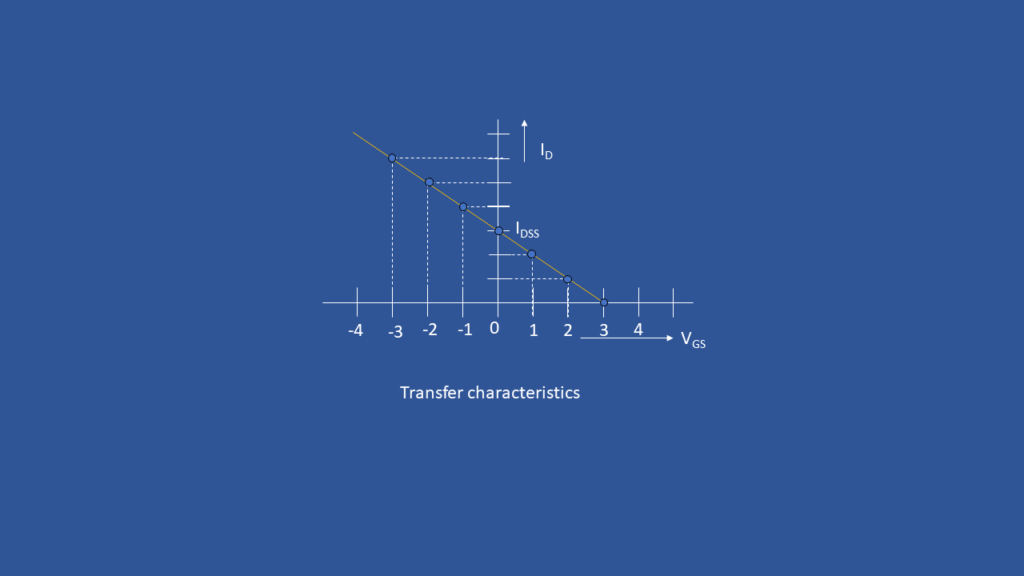
Drain Characteristics of MOSFET


Meru dhavudhu sir
Hahaha… Thank you